Microscopy Solutions for Microbiology
Microscopy applications for your laboratory
Created by Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH
The pioneer of modern bacteriology, German physician and microbiologist Robert Koch, was the first to identify the specific causative agents of tuberculosis, cholera, and anthrax by isolating pure bacterial cultures for which he was awarded a Nobel Prize in medicine.
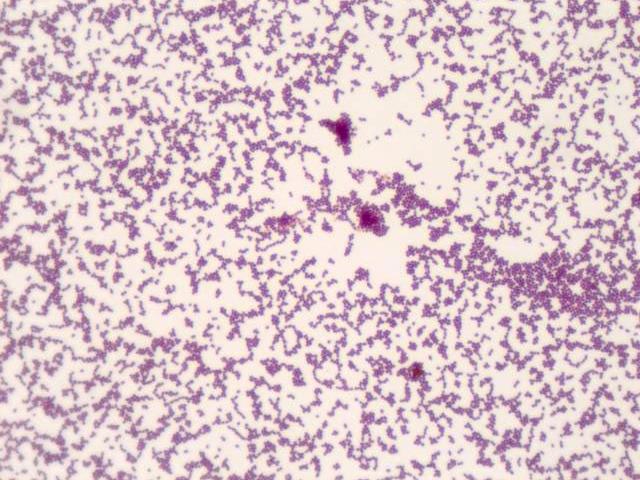
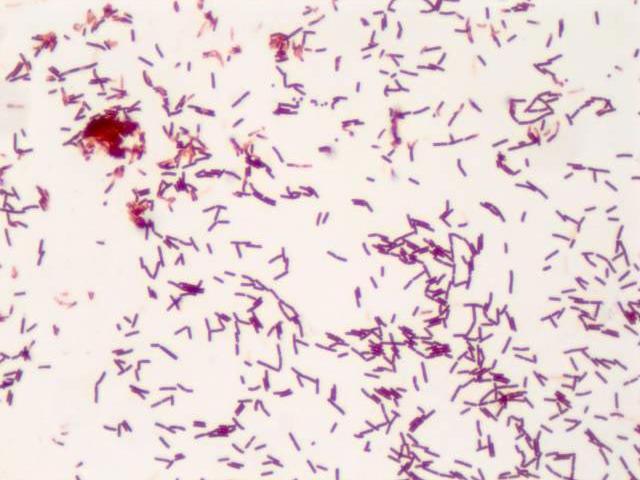
The primary method used for isolation of infectious diseases in the laboratory is microbiological culture. Tissue or fluid samples are tested for the presence of a specific pathogen, which is determined by in vitro growth in a selective or differential medium. The medium can either be a solid culture (as for most bacteria and fungi), a liquid culture (for certain parasites) or a cell culture (usually for virus tests). Once the pathogen has been isolated, it can be examined under a light microscope. Here, the contrast can be improved with various non-specific or specific staining agents. For example, Gram staining can be used to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria due to their different cell wall compositions
Microscopy Solutions for Microbiology
Microscope Requirements
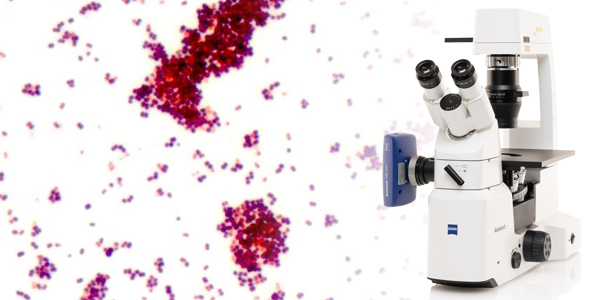
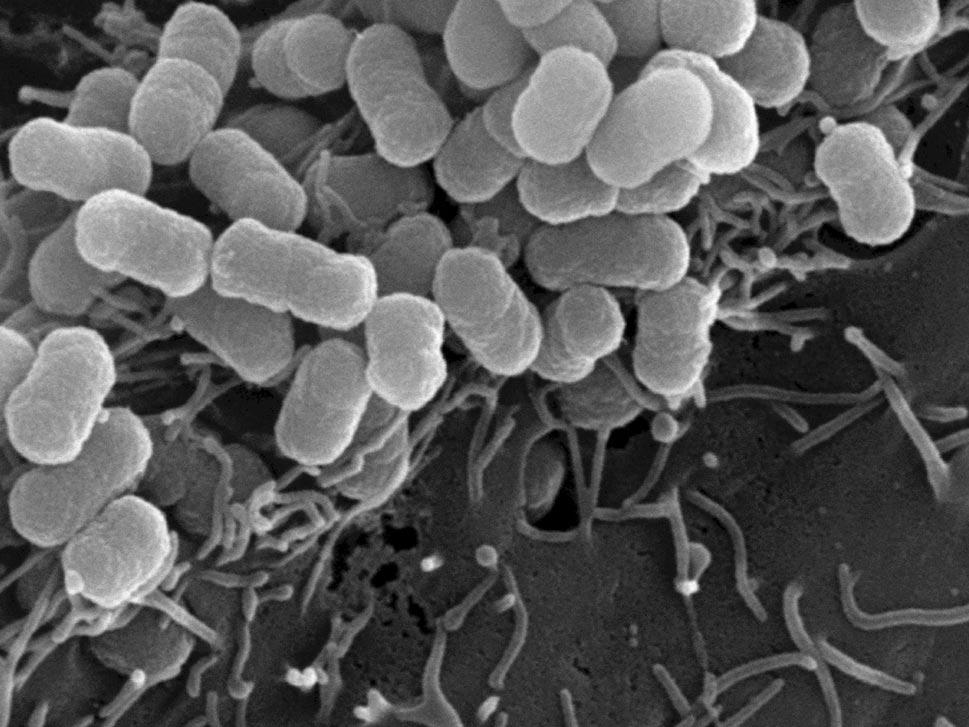
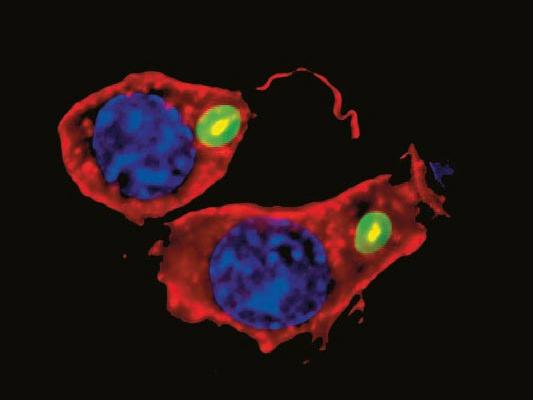
As most pathogens are very small (the average diameter of bacteria is between 0.2 and 2.0 micrometer) the light microscope not only needs to feature high magnifications but also oil immersion objectives to improve morphological examinations when differentiating between cocci (spheres), rods (bacilli) and spirals (spirochetes). Even higher specificity can be achieved with fluorescence microscopy, either unspecific for tuberculosis identification or highly specific with antibody-coupled immunofluorescence and FISH (fluorescence in-situ hybridization).
A very good differentiation of bacterial cell types and clearly visible cellular details are absolute prerequisites in microbiology. Microbiologists rely on crystal-clear images to examine cysts, protozoa and worm eggs in stool samples, Plasmodia in blood samples, or mycobacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms. For microscopic examination brightfield, phase contrast, darkfield, fluorescence, immunofluorescence, or FISH microscopy techniques are used. The optical quality of the microscope, the image fidelity of the attached camera for digital documentation, and the ergonomic design of the instrument can make the difference when screening patient samples efficiently.